
Mechanical Failure Analysis
Define
A backyard porch deck experienced a sudden, unexpected structural failure when a critical turnbuckle—responsible for maintaining static support—snapped after 18 years of service.
-
Turnbuckle failure posed immediate safety hazards
-
Original specifications and maintenance history were unavailable
-
Root cause of failure was uncertain, demanding forensic investigation
Current State: Turnbuckle Reliability
Turnbuckles maintain tension in load-bearing structures, but long-term fatigue, material degradation, and environmental exposure can compromise performance. Without historical data, predicting failure modes is extremely challenging.
Structural & Safety Consequences
-
Immediate risk of collapse and personal injury
-
Unknown load capacity for remaining deck components
-
Potentially costly replacement and liability exposure
Homeowners requested a forensic investigation to determine the cause of failure and provide guidance for safer structural designs.


Goal
Lead a full forensic engineering investigation to:
-
Identify the root cause of turnbuckle failure
-
Determine contributing factors including material, geometry, and loading
-
Extract insights to guide safer, fatigue-resistant design strategies for future structures
Mission: Ensure long-term structural reliability through evidence-based forensic engineering, even under incomplete data conditions.
Approach
Empathize
-
Gathered historical context from the deck owner
-
Documented installation, usage patterns, and environmental exposure
-
Mapped real-world constraints including long-term static loading, weather exposure, and maintenance gaps
Define Core Engineering Problem
Determine why the turnbuckle failed after nearly two decades and identify the mechanism of fracture without original specifications.
Investigation Goals
-
Identify fracture origin and propagation path
-
Evaluate all plausible failure modes: stress corrosion cracking, tensile overload, manufacturing defects, fatigue
-
Integrate hands-on experimental evidence with engineering analysis
-
Deliver actionable insights for material selection and structural design
Ideate / Hypothesis Generation
-
Considered multiple failure mechanisms:
-
Stress corrosion
-
Tensile overload
-
Material or manufacturing defects
-
Fatigue
-
-
Developed testable hypotheses linking observed fracture features to potential causes
Prototype / Experimental Investigation
-
Conducted visual and optical microscopy to document fracture morphology
-
Used Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM) to distinguish brittle vs. ductile fracture features and locate crack origins
-
Applied Energy-Dispersive X-ray Spectroscopy (EDS) to confirm alloy composition
-
Performed fatigue analysis to link crack propagation to cyclic loading patterns
Test
-
Compared fracture patterns to reference materials and failure mode benchmarks
-
Quantified critical crack sizes and stress intensity factors
-
Evaluated evidence against each hypothesized failure mode
Iterate
-
Refined understanding as data ruled out hypotheses (stress corrosion, overload, defects)
-
Focused on fatigue as the dominant failure mechanism
-
Synthesized experimental observations with calculations to confirm root cause


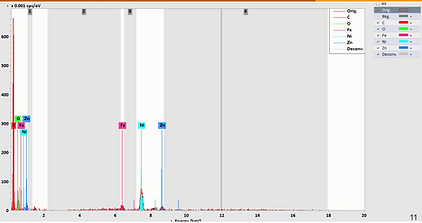



Impact
-
Turnbuckle failure caused by fatigue crack propagation, culminating in sudden fracture
-
Material choice (zinc-aluminum alloy) and load limitations were key contributing factors
-
Provided actionable guidance for improved material selection, design margins, and maintenance strategies

Key Takeaways
-
Demonstrates advanced proficiency in forensic engineering, microscopy, and failure analysis
-
Shows ability to translate ambiguous, real-world structural problems into precise mechanical understanding
-
Emphasizes importance of material evaluation, fatigue design, and proactive maintenance
-
Highlights evidence-based decision-making to prevent catastrophic structural failures
This project reflects my approach to engineering: analyze meticulously, investigate systematically, and engineer solutions informed by real-world evidence.